Hazardous Products Regulations (SOR/2015-17)
Full Document:
- HTMLFull Document: Hazardous Products Regulations (Accessibility Buttons available) |
- XMLFull Document: Hazardous Products Regulations [569 KB] |
- PDFFull Document: Hazardous Products Regulations [1196 KB]
Regulations are current to 2024-11-26 and last amended on 2022-12-15. Previous Versions
PART 7Physical Hazard Classes (continued)
SUBPART 12Substances and Mixtures Which, in Contact with Water, Emit Flammable Gases
General Provision
Marginal note:Interpretation
7.12 In this Subpart, substances and mixtures which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases are liquids and solids that, by interaction with water, are liable to become spontaneously flammable or give off flammable gases in dangerous quantities, that is, in quantities that are greater than one litre of gas per kilogram of the mixture or substance per hour.
Classification in a Category of the Class
Marginal note:Exclusions
7.12.1 (1) The following liquids or solids need not be classified in any category of this hazard class:
(a) those that have a chemical structure that does not contain metals or metalloids;
(b) those that have been shown, through accumulated experience in production or handling, not to react with water; and
(c) those that are soluble in water to form a stable mixture.
Marginal note:Categories
(2) A liquid or solid which, in contact with water, emits flammable gases is classified in a category of this hazard class, based on results from testing performed in accordance with test N.5 of sub-section 33.5.4 of Part III of the Manual of Tests and Criteria, in accordance with the following table:
TABLE
Column 1 Column 2 Item Category Criteria 1 Substances and Mixtures Which, in Contact with Water, Emit Flammable Gases — Category 1 A liquid or solid that
(a) reacts with water at ambient temperature and produces a gas that is liable to ignite spontaneously;
(b) reacts with water at ambient temperature such that the rate of evolution of flammable gas is ≥ 10 l/kg of liquid or solid over any one minute; or
(c) reacts with water at ambient temperature to ignite spontaneously in any step of the test procedure
2 Substances and Mixtures Which, in Contact with Water, Emit Flammable Gases — Category 2 A liquid or solid that reacts with water at ambient temperature such that the maximum rate of evolution of flammable gas is ≥ 20 l/kg of liquid or solid per hour 3 Substances and Mixtures Which, in Contact with Water, Emit Flammable Gases — Category 3 A liquid or solid that reacts with water at ambient temperature such that the maximum rate of evolution of flammable gas is > 1 l/kg of liquid or solid per hour
SUBPART 13Oxidizing Liquids
Definition
Definition of oxidizing liquid
7.13 In this Subpart, oxidizing liquid means a liquid, whether or not combustible, that is liable to cause or contribute to the combustion of other material.
Classification in a Category of the Class
Marginal note:Exclusions
7.13.1 (1) The following liquids need not be classified in any category of this hazard class:
(a) any organic liquid that does not contain oxygen, fluorine or chlorine;
(b) any organic liquid that contains oxygen, fluorine or chlorine if those elements are chemically bonded only to carbon or hydrogen; and
(c) any inorganic liquid that does not contain oxygen or halogens.
Marginal note:Categories
(2) An oxidizing liquid is classified in a category of this hazard class, based on results from testing performed in accordance with test O.2 of sub-section 34.4.2 of Part III of the Manual of Tests and Criteria, in accordance with the following table:
TABLE
Column 1 Column 2 Item Category Criteria 1 Oxidizing Liquids — Category 1 A liquid that, when tested in a 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, spontaneously ignites, or exhibits a mean pressure rise time < the mean pressure rise time of a 1:1 mixture, by mass, of 50.0% perchloric acid and cellulose 2 Oxidizing Liquids — Category 2 A liquid that, when tested in a 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, exhibits a mean pressure rise time ≤ the mean pressure rise time of a 1:1 mixture, by mass, of 40.0% aqueous sodium chlorate solution and cellulose 3 Oxidizing Liquids — Category 3 A liquid that, when tested in a 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, exhibits a mean pressure rise time ≤ the mean pressure rise time of a 1:1 mixture, by mass, of 65.0% aqueous nitric acid and cellulose
SUBPART 14Oxidizing Solids
Definition
Definition of oxidizing solid
7.14 In this Subpart, oxidizing solid means a solid, whether or not combustible, that is liable to cause or contribute to the combustion of other material.
Classification in a Category of the Class
Marginal note:Exclusions
7.14.1 (1) The following solids need not be classified in any category of this hazard class:
(a) any organic solid that does not contain oxygen, fluorine or chlorine;
(b) any organic solid that contains oxygen, fluorine or chlorine if those elements are chemically bonded only to carbon or hydrogen; and
(c) any inorganic solid that does not contain oxygen or halogens.
Marginal note:Categories
(2) An oxidizing solid is classified in a category of this hazard class, based on results from testing performed in accordance with test O.1 of sub-section 34.4.1 of Part III of the Manual of Tests and Criteria or test O.3 of sub-section 34.4.3 of that Part, in accordance with the following table:
TABLE
Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Item Category Criteria Using Test O.1 Criteria Using Test O.3 1 Oxidizing Solids — Category 1 A solid that, when tested in a 4:1 or 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, exhibits a mean burning time < the mean burning time of a 3:2 mixture, by mass, of potassium bromate and cellulose A solid that, when tested in a 4:1 or 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, exhibits a mean burning rate > the mean burning rate of a 3:1 mixture, by mass, of calcium peroxide and cellulose 2 Oxidizing Solids — Category 2 A solid that, when tested in a 4:1 or 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, exhibits a mean burning time ≤ the mean burning time of a 2:3 mixture, by mass, of potassium bromate and cellulose A solid that, when tested in a 4:1 or 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, exhibits a mean burning rate ≥ the mean burning rate of a 1:1 mixture, by mass, of calcium peroxide and cellulose 3 Oxidizing Solids — Category 3 A solid that, when tested in a 4:1 or 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, exhibits a mean burning time ≤ the mean burning time of a 3:7 mixture, by mass, of potassium bromate and cellulose A solid that, when tested in a 4:1 or 1:1 mixture, by mass, with cellulose, exhibits a mean burning rate ≥ the mean burning rate of a 1:2 mixture, by mass, of calcium peroxide and cellulose
SUBPART 15Organic Peroxides
Definitions
Marginal note:Definitions
7.15 The following definitions apply in this Subpart.
- as packaged
as packaged means packaged in the form and condition described in test series B, D, G and H of Part II of the Manual of Tests and Criteria. (tel qu’il est emballé)
- explosive properties
explosive properties means the properties of an organic peroxide that, in laboratory testing according to test series A, C or E of Part II of the Manual of Tests and Criteria, make the liquid or solid liable to detonate, deflagrate rapidly or show a violent effect when heated under confinement. (propriétés explosives)
- organic peroxide
organic peroxide means an organic liquid or solid that contains the bivalent -O-O- structure. (peroxyde organique)
Classification in a Category of the Class
Marginal note:Exclusions
7.15.1 (1) An organic peroxide that contains any of the following need not be classified in any category of this hazard class:
(a) not more than 1.0% available oxygen from the organic peroxides when containing not more than 1.0% hydrogen peroxide; or
(b) not more than 0.5% available oxygen from the organic peroxides when containing more than 1.0% but not more than 7.0% hydrogen peroxide.
Marginal note:Available oxygen content
(2) The available oxygen content, in percent, of an organic peroxide mixture referred to in paragraph (1)(a) or (b) is determined by the following formula:
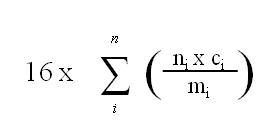
where
- ni
- is the number of peroxygen groups per molecule of organic peroxide i;
- ci
- is the concentration (mass %) of organic peroxide i; and
- mi
- is the molecular mass of organic peroxide i.
Marginal note:Categories
(3) An organic peroxide is classified in a category of this hazard class, based on results from testing performed in accordance with test series A to H of Part II of the Manual of Tests and Criteria, in accordance with the following table:
TABLE
Column 1 Column 2 Item Category Criteria 1 Organic Peroxides — Type A A liquid or solid that, as packaged, is liable to detonate, or deflagrate rapidly 2 Organic Peroxides — Type B A liquid or solid that possesses explosive properties and, as packaged, neither detonates, nor deflagrates rapidly, but is liable to undergo a thermal explosion in that package 3 Organic Peroxides — Type C A liquid or solid that possesses explosive properties and, as packaged, neither detonates, nor deflagrates rapidly, nor undergoes a thermal explosion in that package 4 Organic Peroxides — Type D In laboratory testing, a liquid or solid that
(a) detonates partially, but does not deflagrate rapidly and shows no violent effect when heated under confinement;
(b) does not detonate, but deflagrates slowly and shows no violent effect when heated under confinement; or
(c) neither detonates nor deflagrates, but shows a medium effect when heated under confinement
5 Organic Peroxides — Type E In laboratory testing, a liquid or solid that neither detonates nor deflagrates, and shows low or no effect when heated under confinement 6 Organic Peroxides — Type F In laboratory testing, a liquid or solid that neither detonates in the cavitated state nor deflagrates and
(a) shows low or no effect when heated under confinement, as well as low or no explosive power; or
(b) shows no effect when heated under confinement nor any explosive power, and either
(i) has a SADT < 60°C when evaluated in a 50 kg package, or
(ii) in the case of a liquid mixture, has a diluent that is used for desensitization with a boiling point < 150°C
7 Organic Peroxides — Type G In laboratory testing, a liquid or solid that neither detonates in the cavitated state nor deflagrates, shows no effect when heated under confinement nor any explosive power, and either
(a) has a SADT ≥ 60°C when evaluated in a 50 kg package, or
(b) in the case of a liquid mixture, has a diluent that is used for desensitization with a boiling point ≥ 150°C
Marginal note:Mixtures — organic peroxides
(4) Subject to subsection (5), a mixture of organic peroxides must be classified in the same category as the most hazardous organic peroxide in the mixture, unless data of the types referred to in subparagraph 2.1(a)(i) or (ii) or (b)(i) or (ii) are available for the mixture as a whole and the data support the conclusion that the mixture must be classified in a category that represents a less severe hazard.
Marginal note:Mixtures — Type G organic peroxides
(5) A mixture of two or more Type G organic peroxides must be classified in the category “Organic Peroxides — Type G”, unless the self-accelerating decomposition temperature of the mixture results in the mixture being classified in a category that represents a more severe hazard.
- Date modified: