Output-Based Pricing System Regulations
SCHEDULE 3(Subsections 17(2) to (4), and 20(2), (4) and (5), paragraphs 31(1)(a) and (b), subsection 32(1), paragraphs 34(1)(b) and (c) and Schedule 1)Quantification Requirements
PART 1Bitumen and Other Crude Oil Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.363(k) | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | WCI Method WCI.365 |
| 3 | Wastewater emissions from | ||||
| CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(h) | WCI Method WCI.204(h) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 4 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 2Bitumen and Heavy Oil Upgrading
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.133 | WCI Method WCI.134 | WCI Method WCI.135 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.203(d) | WCI Method WCI.204(d) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(a) | WCI Method WCI.204(a) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 3 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(e) | WCI Method WCI.204(e) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 4 | Venting emissions from | ||||
| CO2 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(b) | WCI Method WCI.204(b) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(k) | WCI Method WCI.204(b) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 5 | Wastewater emissions from | ||||
| CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(h) | WCI Method WCI.204(h) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 6 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 3Petroleum Refining
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Venting emissions from | ||||
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(b) | WCI Method WCI.204(b) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2, and CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(c) | WCI Method WCI.204(c) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(m) | WCI Method WCI.204(m) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 3 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.133 | WCI Method WCI.134 | WCI Method WCI.135 | |
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(a) | WCI Method WCI.204(a) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.203(d) | WCI Method WCI.204(d) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(j) | WCI Method WCI.204(i) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 4 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(e) | WCI Method WCI.204(e) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 5 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 6 | Wastewater emissions from | ||||
| CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(h) | WCI Method WCI.204(h) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 7 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 (1) Direct-only complexity weighted barrels (direct-only CWB) is quantified in accordance with the method outlined in the directive entitled CAN-CWB Methodology for Regulatory Support: Public Report, published by Solomon Associates in January 2014.
(2) In the method referred to in subsection (1),
(a) the value of “Sales and Exports of Steam and Electricity” must be set to zero;
(b) the value of “EC Reported CO2e Site Emissions” excludes
(i) the emissions associated with electricity generated at the covered facility, and
(ii) the emissions associated with steam generated but not used by the covered facility;
(c) the value of “Deemed Indirect CO2e Emissions from imported electricity”
(i) includes emissions associated with electricity that is generated and used at the covered facility, and
(ii) is calculated using 0.420 tonnes of CO2e per MWh of electricity bought;
(d) the value of “Deemed Indirect CO2e Emissions from imported steam” is equal to 0; and
(e) the value of the “CWB factor” used to calculate hydrogen generation, in all cases, is 5.7.
PART 4Natural Gas Processing
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from acid gas removal | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.363 (c) | WCI Method WCI.364 | WCI Method WCI.365 |
| 3 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.363(k) | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | WCI Method WCI.365 |
| 4 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 The combined quantity, in cubic metres, of propane and butane set out in paragraph 4(b), column 2, of the table to Schedule 1 is the sum of the quantity of propane, in cubic metres, at a temperature of 15°C and at an equilibrium pressure and the quantity of butane at a temperature of 15°C and at an equilibrium pressure, in cubic metres.
PART 5Natural Gas Transmission
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.353(d) | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | WCI Method WCI.355 |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 (1) Production by the covered facility, expressed in MWh, is the sum of the amounts determined by the following formula for each of the drivers operated by the covered facility:
Px × Lx× Hx
where
- P
- is the rated brake power of driver “x”, expressed in megawatts;
- L
- is the actual annual average percent load of driver “x”, or, if the actual annual average percent load is unavailable, the percentage determined by the formula:
rpmavg /rpmmax
where
- rpmavg
- is the actual annual average speed during operation of driver “x”, expressed in revolutions per minute, and
- rpmmax
- is the maximum rated speed of driver “x”, expressed in revolutions per minute;
- H
- is the number of hours during the compliance period that driver “x” was operated; and
(2) The following definitions apply in this section.
- driver
driver means an electric motor, reciprocating engine or turbine used to drive a compressor. (conducteur)
- rated brake power
rated brake power means the maximum brake power of a driver as specified by its manufacturer either on its nameplate or otherwise. (puissance au frein nominale)
PART 6Hydrogen Gas Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.133 | WCI Method WCI.134 | WCI Method WCI.135 |
| 3 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(e) | WCI Method WCI.204(e) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 4 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 5 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 7Cement and Clinker Production
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | GHGRP 4.A | GHGRP 4.B | GHGRP 4.C |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 The quantity of clinker set out in paragraph 7(a), column 2, of Schedule 1 refers only to clinker that is transported out of the facility.
2 The quantity of grey cement and white cement set out in paragraphs 7(b) and (c), column 2, of Schedule 1 refers only to cement produced from clinker that was produced at that facility and that has not been transported out of the facility.
PART 8Lime Manufacturing
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | GHGRP 3.A | GHGRP 3.B | GHGRP 3.C |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 The quantity of dolomitic lime does not include the dolomitic lime used in the production of speciality lime.
PART 9Glass Manufacturing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.143 | WCI Method WCI.144 | WCI Method WCI.145 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 10Gypsum Product Manufacturing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 11Mineral Wool Insulation Manufacturing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.183 | WCI Method WCI.184 | WCI Method WCI.185 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 12Brick Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.183 | WCI Method WCI.184 | WCI Method WCI.185 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 13Ethanol Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 14Furnace Black Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in able 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.303(b) | WCI Method WCI.304(b) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 3 | Venting emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.303(a)(3) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 4 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.303(a)(4) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 5 | Industrial product use emissions | SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 |
| 6 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 152–methylpentamethylenediamine (MPMD) Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.133 | WCI Method WCI.134 | WCI Method WCI.135 |
| 3 | Industrial product use emissions | SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 |
| 4 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(e) | WCI Method WCI.204(e) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 5 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 6 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 16Nylon Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 17Petrochemicals Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.303(b) | WCI Method WCI.304(b) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 3 | Venting emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.303(a)(3) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 4 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Methods WCI.303(a)(1), (a)(2) and (c) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 5 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.303(a)(4) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 6 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 7 | Industrial product use emissions | SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 |
| 8 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 18Vaccine Production
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Leakage emissions | SF6 | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 Production is quantified at the end of the formulation step of the manufacturing process, in litres of vaccine, as follows:
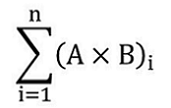
where:
- A
- is the capacity of each tank “i” that is used to combine ingredients at that step, expressed in litres;
- B
- is the number of batches produced in tank “i”; and
- i
- is the ith tank where “i” goes from 1 to n where n is the total number tanks used to combine ingredients.
PART 19Scrap-based Steel Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.5 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.6 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.9 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 20Integrated Steel Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.2 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.3 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.7 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.5 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.8 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.9 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.6 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| 3 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI. 205 |
| 4 | Industrial product use emissions | SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI. 235 |
| 5 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 21Iron Ore Pelletizing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions (induration furnace) | CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.1 | GHGRP 6.C | GHGRP 6.D |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 22Metal Tube Manufacturing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 23Base Metal Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4, and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.163 | WCI Method WCI.164 | WCI Method WCI.165 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.243 | WCI Method WCI.244 | WCI Method WCI.245 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.263 | WCI Method WCI.264 | WCI Method WCI.265 | |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 24Potash Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 25Coal Mining
1 For the purpose of item 2 of Table 1 to this Part, the CH4 leakage emissions from surface coal mining are quantified by multiplying the quantity of coal extracted by the applicable emission factor set out in column 3 of Table 2 to this Part according to the province of extraction set out in column 1 and the coal type set out in column 2 of Table 2.
TABLE 1
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Leakage emissions from | ||||
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.103 | WCI Method WCI.104 | WCI Method WCI.105 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.253 | WCI Method WCI.254 | WCI Method WCI.255 | |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
TABLE 2
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Province | Coal Type | Emission Factor (tonnes of CH4/ tonnes of coal | |
| 1 | Nova Scotia | Bituminous | 7 x 10–5 |
| 2 | New Brunswick | Bituminous | 7 x 10–5 |
| 3 | Saskatchewan | Lignite | 7 x 10–5 |
| 4 | Alberta | Bituminous | 5.5 x 10–4 |
| 5 | Alberta | Sub-bituminous | 2 x 10–4 |
| 6 | British Columbia | Bituminous | 8.6 x 10–4 |
PART 26Production of Metals or Diamonds
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c , 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 27Char Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set outin Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 28Activated Carbon Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 29Nitrogen-based Fertilizer Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| N2O | WCI Method WCI.313 | WCI Method WCI.314 | WCI Method WCI.315 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.83 | WCI Method WCI.84 | WCI Method WCI.85 | |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 30Industrial Potato Processing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 31Industrial Oilseed Processing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 32Alcohol Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 33Wet Corn Milling
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 34Citric Acid Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 35Sugar Refining
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 36Pulp and Paper Production
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
1 For the purposes of the table to this Division, GHGs from stationary fuel combustion emissions from biomass fuels may be quantified using equations 2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-7, 2-8, 2-9, 2-13, 2-14 or 2-18 of the GHGRP, if applicable.
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions from | ||||
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except,
| GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D | |
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | For fossil fuels, GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O, and for pulping liquor, WCI Method WCI.213(c)Footnote for Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types(a) | For fossil fuels, GHGRP 2.C and for pulping liquor, WCI Method WCI.214 | GHGRP 2.D and WCI Method WCI.215 | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 2.A | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D | |
| CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.B, except,
| GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D | |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions: addition of carbonate compound into a lime kiln | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.213(d) | Direct measurement of quantity of carbonate compounds used or indirect measurement using quantity of carbonate compounds according to the quantity on the delivery invoices | WCI Method WCI.215 |
| 3 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 4 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
Return to footnote (a)For the combustion of biomass fuels where CH4 and N2O emission factors are not prescribed, the IPCC Guidelines must be used to estimate those emissions.
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 (1) Production by the covered facility is quantified in tonnes of finished product or tonnes of specialty product, as follows:
(a) in the case of pulp, including dissolving pulp for viscose,
(i) if the moisture content exceeds 10%, the weight of the pulp is adjusted so that its moisture content does not exceed 10%, and
(ii) if the moisture content is equal to or less than 10%, the weight of the pulp without adjustment; and
(b) in the case of a finished product or specialty product referred to in subsection (3) derived directly from pulp or the pulping process, the weight of the product or, if it has been machine dried, its weight after it has been dried.
(2) A finished product referred to in paragraph (1)(b) does not include pulping liquor, wood waste, non-condensable gases, sludge, tall oil, turpentine, biogas, steam, water or products that are used in the production process.
(3) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(b), a specialty product means abrasive paper base, food grade grease resistant paper, packaging waxed paper base, paper for medical applications, napkin paper for commercial use, towel paper for commercial or domestic use, bath paper for domestic use and facial paper for domestic use.
PART 37Automotive Production
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial product use emissions | HFCs | WCI Method WCI.43(d) | WCI Method WCI.44 | WCI Method WCI.45 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 Production is the number of four-wheeled self-propelled vehicles that are designed for use on a highway and that have a gross vehicle weight rating of less than 4 536 kg (10,000 pounds) assembled during a compliance period.
PART 38Electricity Generation
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Stationary Fuel Combustion Emissions
1 (1) CO2, CH4 and N2O from stationary fuel combustion emissions must be quantified by unit in accordance with the following:
(a) for CO2,
(i) in the case of any unit that has obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, sections 20 to 26 of those Regulations,
(ii) in the case of any unit that has not obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations and that generates electricity from the combustion of natural gas, sections 12 to 18 of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, and
(iii) in the case of any other unit, GHGRP 2.A; and
(b) for CH4 and N2O, in the case of all units, GHGRP 2.B.
(2) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(b), for the stationary combustion of diesel, the following emission factors must be used instead of those set out in Table 2-6 to section 2.B of the GHGRP:
(a) for CH4, 0.133 kg/kL; and
(b) for N2O, 0.4 kg/kL.
2 The following sampling, analysis and measurement requirements apply to stationary fuel combustion emissions for each unit:
(a) for CO2,
(i) in the case of any unit that has obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, section 27 of those Regulations,
(ii) in the case of any unit that has not obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations and that generates electricity from the combustion of natural gas, section 19 of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, and
(iii) in the case of any other unit, GHGRP 2.C; and
(b) for CH4 and N2O, in the case of all units, GHGRP 2.C.
3 Replacement data for stationary fuel combustion emissions must be calculated for each unit in accordance with the following:
(a) for CO2,
(i) in the case of any unit that has obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, section 28 of those Regulations,
(ii) in the case of any unit that has not obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations and that generates electricity from the combustion of natural gas, section 20 of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, and
(iii) in the case of any other unit, GHGRP 2.D; and
(b) for CH4 and N2O, in the case of all units, GHGRP 2.D.
Emissions from Other Specified Emission Types
Quantification of GHGs from Other Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Leakage emissions from coal storage | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.103 | WCI Method WCI.104 | WCI Method WCI.105 |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from acid gas scrubbers and acid gas reagent | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.43(c) | WCI Method WCI.44 | WCI Method WCI.45 |
| 3 | Industrial product use emissions from | ||||
| SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 | |
| HFCs | WCI Method WCI.43(d) | WCI Method WCI.44 | WCI Method WCI.45 | |
| 4 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production — Main Industrial Activity
4 (1) Subject to section 5, if a unit uses only one fossil fuel to generate electricity, production of electricity must be quantified in GWh of gross electricity generated by the unit, measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of each unit using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations.
(2) Subject to section 5, if a unit uses a mixture of fossil fuels or a mixture of biomass and fossil fuels to generate electricity, the gross electricity generated by the unit is to be determined separately for the gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels in accordance with the following formula and expressed in GWh:
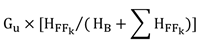
where
- GU
- is the gross quantity of electricity generated by the unit during a compliance period, as measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of the unit using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations, expressed in GWh;
- HFFk
- is determined in accordance with the following formula, calculated separately for gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels type “k”:
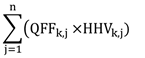
where
- QFFj
- is the quantity of gaseous, liquid or solid fuel, as the case may be, type “j” combusted in the unit to generate electricity during the compliance period, determined in accordance with subsection (3),
- HHVj
- is the higher heating value of the gaseous, liquid or solid fuel, as the case may be, type “j” combusted in the unit, determined in accordance with subsection 24(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, and
- j
- is the jth fossil fuel type combusted in the unit, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the number of types of gaseous, liquid or solid fuel combusted, as the case may be, combusted; and
- HB
- is determined in accordance with the formula
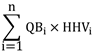
where:
- QBi
- is the quantity of biomass fuel type “i” combusted in the unit to generate electricity during the compliance period, determined in accordance with the subsection (3),
- HHVi
- is the higher heating value for the biomass fuel type “i” combusted in the unit, is determined in accordance with subsection 24(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, and
- i
- is the ith biomass fuel type combusted in the unit, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the number of types of biomass fuels combusted.
(3) The quantity of fuel for QFFj or QBi is determined on the following basis:
(a) for a solid fuel, the mass of the fuel combusted, on a wet or dry basis, expressed in tonnes and measured by a measuring device;
(b) for a liquid fuel, the volume of the fuel combusted, expressed in kL and measured using a flow meter; and
(c) for a gaseous fuel, the volume of the fuel combusted, expressed in standard cubic metres and measured using a flow meter.
5 If a combustion engine unit and a boiler unit share the same steam turbine, the quantity of electricity generated by a given unit is determined in accordance with subsection 11(2) of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity.
DIVISION 3Additional Industrial Activity – Quantification of Production
6 If a covered facility uses only one fossil fuel to generate electricity, production of electricity is quantified in GWh of gross electricity generated through the use of fossil fuels.
7 (1) If a covered facility uses a mixture of fossil fuels or a mixture of biomass and fossil fuels to generate electricity, the gross electricity generated by the facility is to be determined separately for the gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels in accordance with the following formula and expressed in GWh:
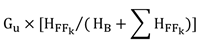
where
- GU
- is the gross quantity of electricity generated by the covered facility during the compliance period, expressed in GWh;
- HFFk
- is determined in accordance with the following formula, calculated separately for gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels type “k”:
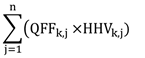
where
- QFFj
- is the quantity of gaseous, liquid or solid fuel, as the case may be, type “j” combusted in the facility for electricity generation during the compliance period, determined under subsection (2) and in accordance with section 2.C.2 of the GHGRP 2.C.2,
- HHVj
- is the higher heating value of the gaseous, liquid or solid fuel, as the case may be, type “j” combusted in the facility for electricity generation determined in accordance with sections 2.C.1 and 2.C.3 of the GHGRP, and
- j
- is the jth fossil fuel type combusted in the facility, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the number of types of gaseous, liquid or solid fuels combusted, as the case may be; and
- HB
- is determined in accordance with the formula
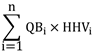
where
- QBi
- is the quantity of biomass fuel type “i” combusted in the facility for electricity generation during the compliance period, determined in accordance with subsection (2) and with section 2.C.2 of the GHGRP and the WCI Method WCI.214,
- HHVi
- is the higher heating value for each biomass fuel type “i” combusted in the facility for electricity generation in accordance with sections 2.C.1 and 2.C.3. of the GHGRP and the WCI Method WCI.214, and
- i
- is the ith biomass fuel type combusted in the facility, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the number of types of biomass fuels combusted.
(2) The quantity of fuel for QFFj and QBi is determined on the following basis:
(a) for a solid fuel, the mass of the fuel combusted, on a wet or dry basis, expressed in tonnes and measured in accordance with section 2.C.2 of the GHGRP;
(b) for a liquid fuel, the volume of the fuel combusted, expressed in kL and measured in accordance with section 2.C.2. of the GHGRP; and
(c) for a gaseous fuel, the volume of the fuel combusted, expressed in standard cubic metres and measured in accordance with section 2.C.2 of the GHGRP 2.C.2.
- Date modified: